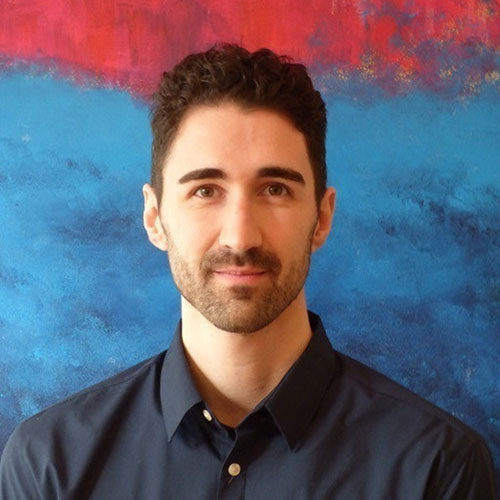
Containers run in isolation and don’t know anything about other processes or containers on the same machine. You have two options to let containers communicate with each other:
- Container Linking (aka legacy linking, deprecated) without any networks involved or
- using Container Networks.
Linking containers is simple to setup, but also limited and should only be used during development.
Option 1: Container Linking (Legacy Linking, deprecated)
Let’s assume you have two containers: The first one is running MongoDB, the second is running NodeJS and you want to connect them via Container Linking. First you give the MongoDB container a name:
# Run container with name docker run -d --name my-mongodb mongo
Then your second container (in this example node) can be linked to it:
# Link node container to my-mongo and choose alias 'mongodb' docker run -d --link my-mongo:mongodb node
The alias mongodb that you chose is now available as a host within the node container:
{
"databaseConfig" : {
"host" : "mongodb",
"database" : "myDatabase"
}
}
You can repeat this process if you want to join more containers.
Option 2: Creating a container network
Containers have networking enabled by default, and they can make outgoing connections. If two containers are on the same network (and only then), they can talk to each other using container IP addresses or container names. You can group containers into their own isolated network.
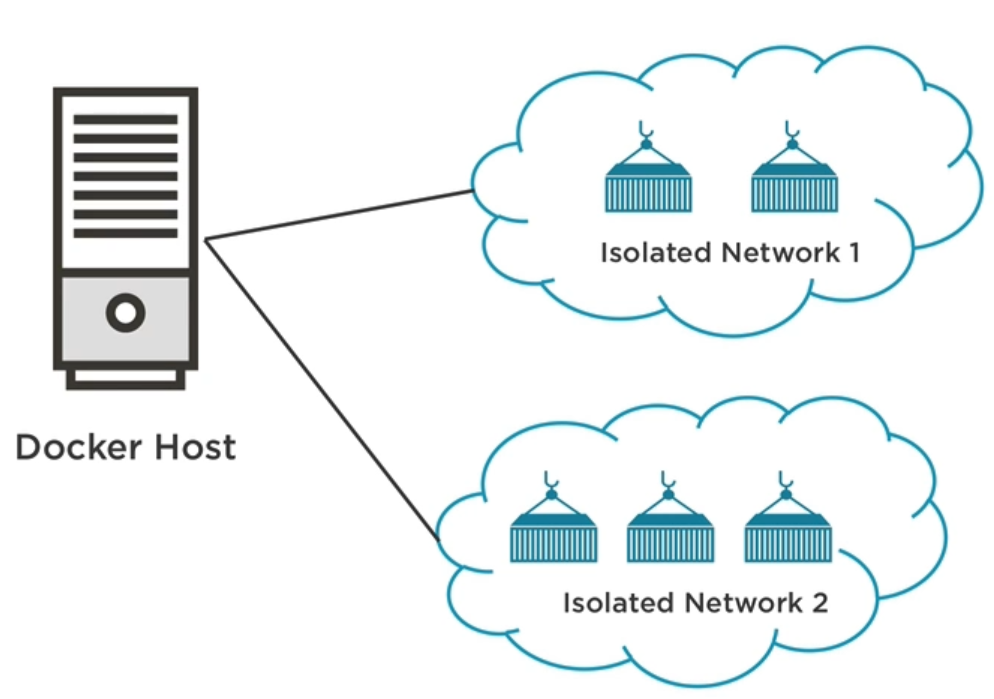
# list networks and their drivers docker network ls # list containers attached to the network, subnet, gateway and others docker network inspect my-network
First you have to create a custom bridge network. After that there are two ways to put a container on a network:
- Assign the network to a container that you start or
- add an already running container to the network.
# create bridged network with name 'isolated-network' docker network create --driver bridge isolated-network
Now, start the first container and attach it to the network:
# run detached container and assign network
docker run -d \
--network isolated-network \
--network-alias mongodb \
mongo
# --network is same as --net
# --network-alias is same as --net-alias
Having network-alias mongodb allows us to connect to this container using mongodb as host name.
Run the second container and attach it to the same network:
# run detached container and assign network
docker run -d \
--network isolated-network \
--network-alias node-app \
node
Docker network drivers
bridge | The default network driver. |
host | Remove network isolation between the container and the Docker host. |
none | Completely isolate a container from the host and other containers. |
overlay | Overlay networks connect multiple Docker daemons together. |
ipvlan | IPvlan networks provide full control over both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. |
macvlan | Assign a MAC address to a container. |
Linking multiple containers
If you have many containers it can be tedious to create networks and attach them to it via command line every time. Instead you should use Docker Compose.
