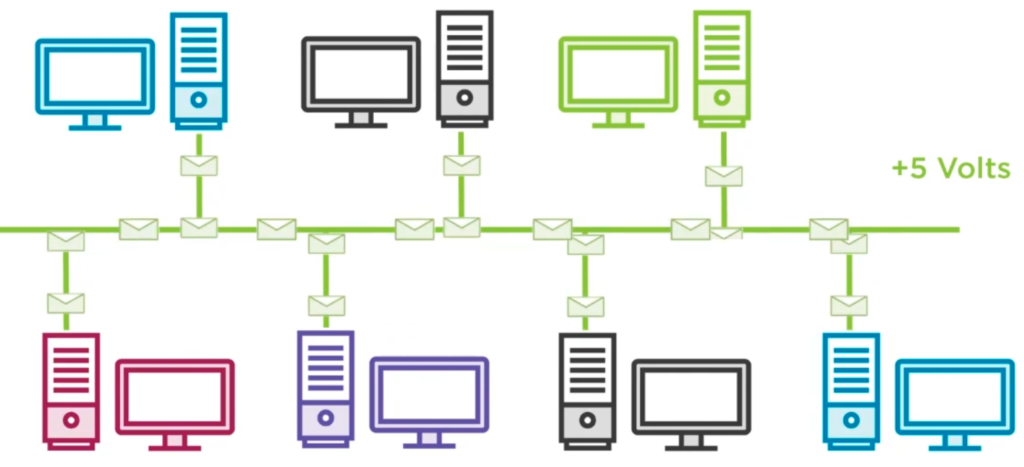
CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection). In an old fashioned Bus structure all connected devices were listening and sending on the same wire one at a time. If a device initiated a communication it sent 5 volt on the cable. A collision could occur by accident if two devices try to send at the same time (= 10 volt). In that case every device stopped communicating and retried after a random amount of seconds.
Half duplex means one device can talk but not listen at the same time. Full duplex mean one device can talk and listen at the same time. In Full duplex you do not have to worry about collisions. Most modern networks are Full Duplex. Ethernet speed evolved from 10 Megabit per second to 100 Gigabit per second in data centers and Wide Area Networks.
An Ethernet frame is the mechanism that transfers data across an Ethernet network since the early 1980ies (actual protocol name is Ethernet II Frame). It is composed of this:

A frame is a chunk of data with a data link layer header referred to as Protocol Data Unit (PDU). Data is usually layer 2 information or layer 3 information in form of IP packets (type field will indicate what type of info). The maximum transmission unit (MTU) defines the maximum amount that can be send per frame, for Ethernet it is 1500 bytes. FCS (frame check sequence) will do a CRC (cyclical redundancy check): It hashes the data and puts the 32 bit hash result in the FCS field, so that the receiver can do the same hash algorithm and check whether data was sent correctly or not.
A MAC is a hardware address consisting of “baked in” ID and serial number: